About the Texas Center for Birth Defects Research and Prevention
 Approximately one in ten infants in the United States are born in Texas. In 1996, the Texas Center for Birth Defects Research and Prevention was established as a part of the Birth Defects Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch of the Texas Department of State Health Services in Austin. The mission of the Texas Center is to conduct population-based epidemiologic research studies to understand the causes of specific birth defects, including participation in the National Birth Defects Prevention Study.
Approximately one in ten infants in the United States are born in Texas. In 1996, the Texas Center for Birth Defects Research and Prevention was established as a part of the Birth Defects Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch of the Texas Department of State Health Services in Austin. The mission of the Texas Center is to conduct population-based epidemiologic research studies to understand the causes of specific birth defects, including participation in the National Birth Defects Prevention Study.
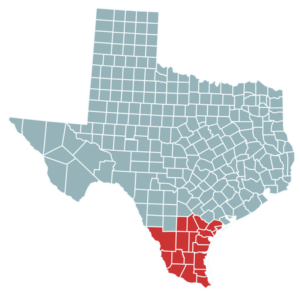
The Texas Center is in a unique position to contribute to our understanding of what causes birth defects, especially due to the 1,200-mile border shared with Mexico. Health disparities between Texans living along the border with Mexico and those in non-border communities have long been a concern for public health officials. The BD-STEPS study area for Texas is the Lower Rio Grande Valley, which encompasses Gulf Coast industrial cities such as Corpus Christi, as well as Cameron and Webb Counties. These two counties on the border with Mexico have experienced some of the country's highest neural tube defect rates.
Team

Dr. Philip Lupo
Principal Investigator
Dr. Lupo is a genetic epidemiologist, Professor of Pediatrics at Baylor College of Medicine, Endowed Chair of Molecular Epidemiology at Texas Children’s Hospital, and Director of the Epidemiology and Population Sciences Program in the Texas Children’s Cancer and Hematology Center. One of Dr. Lupo’sresearch interests is leveraging population-based registry data to inform our understanding of the genetic etiologies of birth defects, as well as cancer risk in individuals with birth defects. He has several ongoing studies focused on birth defects, has been an active investigator in the NBDPS and BD-STEPS, and has held leadership roles in both the National Birth Defects Prevention Network and the Society for Birth Defects Research and Prevention.
BD-STEPS provides an unparalleled collaborative framework to identify novel risk factors for birth defects in diverse populations. Our ultimate goal is to inform novel birth defect prevention efforts, and we are confident that BD-STEPS will contribute to that goal
Dr. Philip Lupo

Dr. Charles Shumate
Principal Investigator
Dr. Shumate, Director of the Birth Defects Epidemiology and Surveillance Branch at Texas Department of State Health Services. One of Dr. Shumate’s research interests is helping to develop a better understanding between social determinants of health and the occurrence of birth defects. He has been a collaborator in the NBDPS and BD-STEPS.
Our center believes the transformative impact of turning data into action, especially for the most vulnerable among us, and BD-STEPS is an opportunity to participate in such an endeavor.
Dr. Charles Shumate
Dr. A.J. Agopian
Principal Investigator
Dr. Agopian is an Associate Professor in the Department of Epidemiology at the UTHealth School of Public Health. Research interests include a broad range of maternal and infant birth defects risk factors, genomics, outcomes among infants with birth defects, and surveillance and classification methodology. In addition to the National Birth Defects Prevention Study (NBDPS) and the Birth Defects Study To Evaluate Pregnancy exposureS (BD-STEPS), Dr. Agopian collaborates with investigators on research over a range of local, national, and international birth defects datasets.
A better understanding of the causes and consequences of birth defects will be paramount to preventing these conditions and improving health among affected individuals. BD-STEPS provides new opportunities for identifying birth defects risk factors and advancing knowledge.
Dr. A.J. Agopian
Notable Research Findings
The following are selected examples of important research publications led by the Texas Center.
Kim, J., Swartz, M. D., Langlois, P. H., Romitti, P. A., Weyer, P., Mitchell, L. E., Luben, T. J., Ramakrishnan, A., Malik, S., Lupo, P. J., Feldkamp, M. L., Meyer, R. E., Winston, J. J., Reefhuis, J., Blossom, S. J., Bell, E., Agopian, A. J., & National Birth Defects Prevention Study (2017). Estimated Maternal Pesticide Exposure from Drinking Water and Heart Defects in Offspring. International journal of environmental research and public health, 14(8), 889. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph14080889
Hoang, T. T., Lei, Y., Mitchell, L. E., Sharma, S. V., Swartz, M. D., Waller, D. K., Finnell, R. H., Benjamin, R. H., Browne, M. L., Canfield, M. A., Lupo, P. J., McKenzie, P., Shaw, G. M., Agopian, A. J., & National Birth Defects Prevention Study (2019). Maternal genetic markers for risk of celiac disease and their potential association with neural tube defects in offspring. Molecular genetics & genomic medicine, 7(6), e688. https://doi.org/10.1002/mgg3.688
Hoang, T. T., Lei, Y., Mitchell, L. E., Sharma, S. V., Swartz, M. D., Waller, D. K., Finnell, R. H., Benjamin, R. H., Browne, M. L., Canfield, M. A., Lupo, P. J., McKenzie, P., Shaw, G., Agopian, A. J., & National Birth Defects Prevention Study (2019). Maternal Lactase Polymorphism (rs4988235) Is Associated with Neural Tube Defects in Offspring in the National Birth Defects Prevention Study. The Journal of nutrition, 149(2), 295–303. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/nxy246
Hoyt, A. T., Ramadhani, T., Le, M. T., Shumate, C. J., Canfield, M. A., Scheuerle, A. E., & National Birth Defects Prevention Study (2020). Acculturation and selected birth defects among non-Hispanic Blacks in a population-based case-control study. Birth defects research, 112(7), 535–554. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdr2.1665
Lei, Y., Ludorf, K. L., Yu, X., Benjamin, R. H., Gu, X., Lin, Y., Finnell, R. H., Mitchell, L. E., Musfee, F. I., Malik, S., Canfield, M. A., Morrison, A. C., Hobbs, C. A., Van Zutphen, A. R., Fisher, S., Agopian, A. J., & National Birth Defects Prevention Study (2020). Maternal hypertension-related genotypes and congenital heart defects. American journal of hypertension, hpaa116. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajh/hpaa116
Patel, J., Nembhard, W. N., Politis, M. D., Rocheleau, C. M., Langlois, P. H., Shaw, G. M., Romitti, P. A., Gilboa, S. M., Desrosiers, T. A., Insaf, T., Lupo, P. J. & National Birth Defects Prevention Study (2020). Maternal occupational exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and the risk of isolated congenital heart defects among offspring. Environmental Research, 186, 109550. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109550
Mohan Dass, N. L., Botto, L. D., Tinker, S. C., Canfield, M. A., Finnell, R. H., Gallaway, M. S., Hashmi, S. S., Hoyt, A. T., Nembhard, W. N., Waller, D. K., & National Birth Defects Prevention Study (2022). Associations between maternal reports of periconceptional fever from miscellaneous causes and structural birth defects. Birth defects research, 10.1002/bdr2.2068. Advance online publication. https://doi.org/10.1002/bdr2.2068
Contact
A.J. Agopian, PhD
Associate Professor
Department of Epidemiology
UTHealth
Birth Defects Office Phone: 512-776-7232
